Kata bahasa Indonesia
English word
TANDA HUBUNG
WORDNET DICTIONARY
CIDE DICTIONARY
OXFORD DICTIONARY
Link, Gadget dan Share 

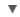
WORDNET DICTIONARY
Noun has 2 senses
- ohm(n = noun.quantity) - a unit of electrical resistance equal to the resistance between two points on a conductor when a potential difference of one volt between them produces a current of one ampere;
- ohm(n = noun.person) georg simon ohm - German physicist who formulated Ohm's law (1787-1854);
Derived form adjective ohmic1
CIDE DICTIONARY
, n. Array
The standard unit in the measure of electrical resistance, being the resistance of a circuit in which a potential difference of one volt produces a current of one ampére. As defined by the International Electrical Congress in 1893, and by United States Statute, it is a resistance substantially equal to 109 units of resistance of the C. G. S. system of electro-magnetic units, and is represented by the resistance offered to an unvarying electric current by a column of mercury at the temperature of melting ice 14.4521 grams in mass, of a constant cross-sectional area, and of the length of 106.3 centimeters. As thus defined it is called the international ohm . [1913 Webster]
OXFORD DICTIONARY
, n. Electr. the SI unit of resistance, transmitting a current of one ampere when subjected to a potential difference of one volt.
Derivative
ohmage n.
Etymology
G. S. Ohm, Ger. physicist d. 1854



