Kata bahasa Indonesia
English word
TANDA HUBUNG
WORDNET DICTIONARY
CIDE DICTIONARY
OXFORD DICTIONARY
Link, Gadget dan Share 

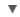
WORDNET DICTIONARY
Noun has 1 sense
- karyokinesis(n = noun.process) - organic process consisting of the division of the nucleus of a cell during mitosis or meiosis;
Derived form adjective karyokinetic1
CIDE DICTIONARY
, n. Array
- The indirect division of cells in which, prior to division of the cell protoplasm, complicated changes take place in the nucleus, attended with movement of the nuclear fibrils; -- opposed to
karyostenosis . The nucleus becomes enlarged and convoluted, and finally the threads are separated into two groups which ultimately become disconnected and constitute thedaughter nuclei . Called alsomitosis . SeeCell development , under Cell. [1913 Webster] - The changes that occur in the nucleus of a cell, especially movements of the chromosomes, in the process of cell division. [PJC]
OXFORD DICTIONARY
, n. Biol. the division of a cell nucleus during mitosis.
Etymology
KARYO- + Gk kinesis movement f. kineo move



