Kata bahasa Indonesia
English word
TANDA HUBUNG
WORDNET DICTIONARY
CIDE DICTIONARY
OXFORD DICTIONARY
Link, Gadget dan Share 

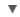
WORDNET DICTIONARY
Noun has 1 sense
- carburettor(n = noun.artifact) carburetor - mixes air with gasoline vapor prior to explosion;
CIDE DICTIONARY
, n.
- An apparatus in which coal gas, hydrogen, or air is passed through or over a volatile hydrocarbon, in order to confer or increase illuminating power. [1913 Webster]
- One that carburets; specif., an apparatus in which air or gas is carbureted, as by passing it through a light petroleum oil. The carburetor for a gasoline engine is usually either a
surface carburetor float carburetor float-feed carburetor or spray carburetor
OXFORD DICTIONARY
, n. (also carburetter, US carburetor) an apparatus for carburation of petrol and air in an internal-combustion engine.
Etymology
as CARBURET + -OR(1)
See related words and definitions of word "" in Indonesian 




