Kata bahasa Indonesia
English word
TANDA HUBUNG
WORDNET DICTIONARY
CIDE DICTIONARY
OXFORD DICTIONARY
Link, Gadget dan Share 

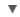
WORDNET DICTIONARY
Noun has 2 senses
- thymus(n = noun.plant) genus thymus - large genus of Old World mints: thyme;
- thymus(n = noun.body) thymus gland - a ductless glandular organ at the base of the neck that produces lymphocytes and aids in producing immunity; atrophies with age;
CIDE DICTIONARY
, a. Array
Of, pertaining to, or designating, the thymus gland. [1913 Webster]
OXFORD DICTIONARY
, n. (pl. thymi) (in full thymus gland) Anat. a lymphoid organ situated in the neck of vertebrates (in humans becoming much smaller at the approach of puberty) producing lymphocytes for the immune response.
Etymology
mod.L f. Gk thumos



